Building Dynamic Pagination in React: Server-Side Fetching with Client Components
Apr 28 • 3 min read
Building Dynamic Pagination in React: Server-Side Fetching with Client Components
Pagination is a core feature for any application dealing with a large amount of data: product listings, blog posts, user lists, etc.
Today, we'll explore how to implement dynamic pagination that fetches data from the server page-by-page, while keeping the UI fast and smooth with React Client Components.
Why Use Dynamic Pagination?
Dynamic pagination means:
- Fetching only a subset of data (e.g., 10 items at a time) from the server.
- Avoiding loading all data at once (which slows down apps).
- Improving load times, SEO, and UX.
- Reducing server load and bandwidth consumption.
Perfect for ecommerce stores, blogs, dashboards, admin panels, etc.
How Pagination Works (At a High Level)
- User visits the page.
- Frontend sends a request to the server with a page number.
- Server sends back only the relevant items.
- Frontend renders them dynamically.
- User can navigate between pages, triggering new fetches.
Setting Up the Backend (Fake API Example)
Your backend route might look like this:
Returns:
You need items and total count to calculate how many pages there are.
Frontend: React Pagination Example
Let's build a dynamic pagination system using React client components.
1. Create a Pagination Service
2. Create a PaginatedList Component
Key Features of This Setup
-
Server-Side Fetching:
- Each page fetches only needed items.
- Saves bandwidth and improves speed.
-
Client Components:
- Handles navigation and user interaction instantly.
- Fetches new data only when needed (on page change).
-
Graceful State Handling:
- Disable buttons when you reach first or last page.
- Smooth user experience without page reloads.
Server-Side vs Client-Side Pagination: When to Use
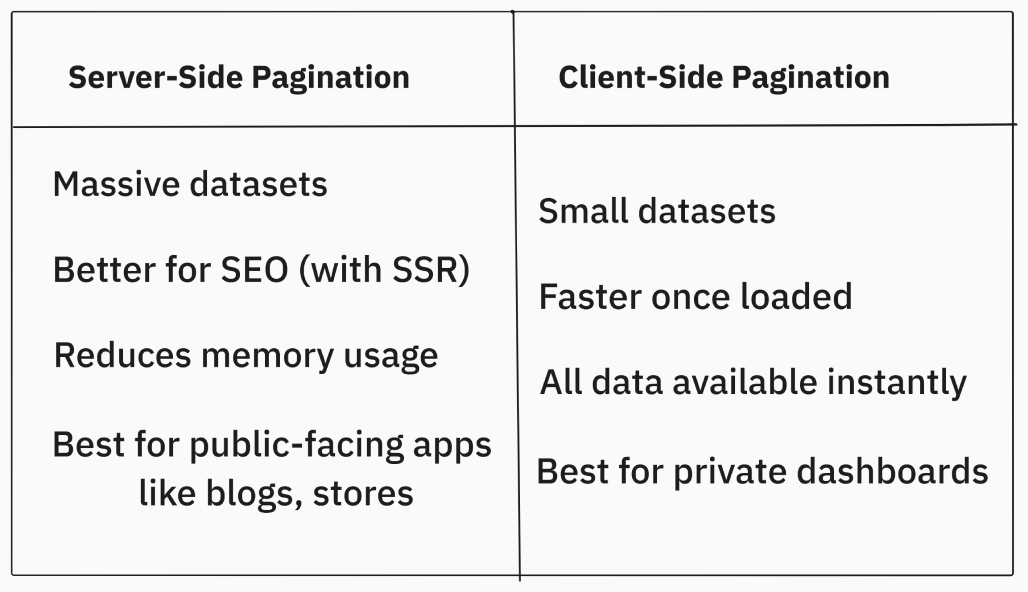
Conclusion
Dynamic pagination is an essential building block for scalable, fast, and user-friendly React applications.
By fetching data page-by-page from the server and rendering them smoothly using client-side components, you keep your app lightweight and your users happy.
Start simple — but always keep in mind:
- Proper state management
- Loading states and error handling
- Optimizing API efficiency
Pagination isn't just about navigation — it's about performance. 🚀
Build it right, and your app will scale effortlessly, even when you have millions of records!